GST is a single tax on the supply of goods and services, right from the manufacturer to the consumer. The Input Tax credit paid at each stage will be available in the subsequent stage of value addition, which makes GST essentially a tax only on value addition at each stage. It is the end consumer who will bear only the GST charged by the last dealer in the supply chain, with set-off benefits at all the previous stages. With the streamlining of the multiple taxes, the final cost to the consumer will turn out to be low because of elimination of double charging system.
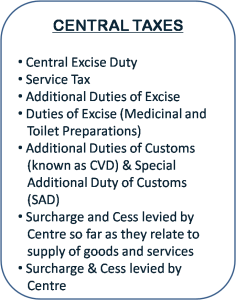
Taxes to be subsumed
Taxes not to be subsumed
- Basic Customs Duty
- Road and Passenger Tax
- Stamp Duty
- Export Duty
- Electricity Duty
- Property Tax
- Toll Tax
Meaning & Scope of Supply
Supply includes:
(a)All forms of supply of goods and/or services such as sale, transfer, barter, exchange, license, rental, lease or disposal made or agreed to be made for a consideration by a person in the course or furtherance of business,
(b) Importation of services, whether or not for a consideration and whether or not in the course or furtherance of business, and
(c) A supply made or agreed to be made without a consideration(SCH-I).
Inward Supply:
“Inward Supply” in relation to a person, shall mean receipt of goods and/or services whether by purchase, acquisition or any other means and whether or not for any consideration.
Outward Supply
“Outward Supply” in relation to a person, shall mean the supply of goods and/or services, whether, by sale, transfer, barter, exchange, license, rental, lease or disposal made or agreed to be made by such person in the course or furtherance of business.
Continuous Supply
Means a supply of services which is provided, or agreed to be provided, continuously or on the recurrent basis, under a contract, for a period exceeding three months with periodic payment obligations and includes the supply of such services as the Government may, subject to such conditions, by notification, specify.
Composite Supply
A supply made by a taxable person to a recipient comprising two or more supplies of goods or services, or any combination thereof, which are naturally bundled and supplied in conjunction with each other in the ordinary course of trade, one of which is a principal supply.
Illustration
Where goods are packed and transported with insurance, the supply of goods, packing materials, transport and insurance is a composite supply and supply of goods is the principal supply.
Mixed Supply
Means: Two or more individual supplies of goods or services, or any combination thereof, made in conjunction with each other by a taxable person for a single price where such supply does not constitute a composite supply.
Illustration
A supply of a package consisting of canned foods, sweets, chocolates, cakes, dry fruits, aerated drink and fruit juices when supplied for a single price is a mixed supply. Each of these items can be supplied separately and is not dependent on any other. It shall not be a mixed supply if these items are supplied separately.
Taxability:
The tax liability on a mixed supply comprising two or more supplies shall be treated as a supply of that particular supply which attracts the highest rate of tax.
Principal Supply
The supply of goods or services which constitutes the predominant element of a composite supply and to which any other supply forming part of that composite supply is ancillary and does not constitute, for the recipient an aim in itself, but a means for better enjoyment of the principal supply.
Zero Rated Supply
Means export of goods or services or both; or supply of goods or services or both to a Special Economic Zone developer or a Special Economic Zone unit (eligible for ITC).
Exempt Supply
- Supply of any goods and/or services which are NOT TAXABLE under this Act
- Supply of goods and/or services under this Act which attracts NIL rate of tax or which may be exempt from tax (Non-Taxable Supply)
Time of Supply-Goods & Services
General Rule
Time of supply of goods could be the earlier of the following:
- The date of issue of the invoice with respect to the supply; or
- The date on which the supplier receives the payment.
- Where it is not possible to determine the Time of Supply, then Time of Supply would be:
(i) In case where Return to be filed, then the date on which Return to be filed.
(ii) In any other case on which CGST/SGST is paid.
Activities which are not supply under GST
Activities and transactions specified in Schedule III –
- Services by an employee to the employer in the course of or in relation to his employment;
- Services of funeral, burial, crematorium or mortuary including transportation of the deceased.
- Actionable claims, other than lottery, betting and gambling
- Sale of land / Sale of building after occupation or completion will not attract GST. Thus, sale of building before completion or before occupancy will attract GST
Such activities or transactions undertaken by the Central Government, a State Government or any local authority in which they are engaged as public authorities, as may be notified by the Government on the recommendations of the Council.
Invoicing
Raising of invoices will be the most crucial part of the GST Regime. It will be the basis on which rightful inputs can be availed.
The absence or wrong filing of required information could trigger denial or delay in claiming input tax credit.
In the GST regime, two types of invoices will be issued:
1.Tax invoice
2.Bill of supply
Tax invoice
When a registered taxable person supplies taxable goods or services, a tax invoice is issued.
- There are 16 particulars that are required to be filled up in the invoice, these include:
– HSN (Harmonised System of Nomenclature) code,
– 15-digit goods and services taxpayer identification number
(GSTIN) of the recipient; and
– the state code in which the delivery has been made.
- For generating the invoice, variety of transactions needs to be captured , such as:
– services on inter-company basis,
– stock transfer and receipt of advances; and
– centralised procurements for re-distribution
GST Working Model
- How a particular transaction of goods and services would be taxed simultaneously under Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST)?
- The Central GST and the State GST would be levied simultaneously on
every transaction of supply of goods and services except the
exempted goods and services.
- Further, both would be levied on the same price or value
- While the location of the supplier and the recipient within the
country is immaterial for the purpose of CGST, however, SGST would
be chargeable only when the supplier and the recipient are both
located within the State.
How GST will operate under Integrated GST (GST)?
- Integrated GST (IGST) would be levied and collected by the Centre on inter-State supply of goods and services.
- The GST on supplies in the course of Inter-State trade or commerce shall be levied and collected by the Government of India.
- Such tax shall be apportioned between the Union and the States in the manner as may be provided by the law.
Persons liable to be Registered in GST
- Every supplier who makes a taxable supply of goods and / or services liable to get himself registered in the state from where he supplies
- Threshold limit (computed on all India basis)
–Special category states – Rs.10 lakhs
–Other states –Rs.20 lakhs
- Application to be made within 30 days
- PAN based Registration
Following persons to obtain registration irrespective of their threshold limit:
–Persons making inter-state taxable supply
–Casual taxable persons
–Non-resident taxable persons
–Persons acting as agents or who supply on behalf of other taxable persons
–Input service distributor
–Electronic commerce operator
–Persons who supply through electronic commerce operator
Exemption from Registration:
- Persons dealing in goods and/services that are not liable to tax or are exempted under GST Act
- Agriculturists
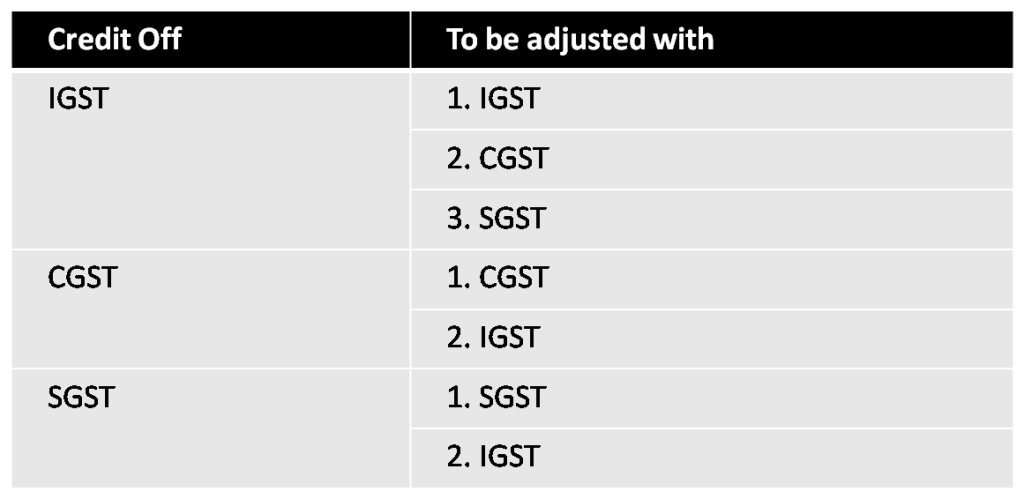
How to adjust Input Tax Credit (ITC) ?
Setoff of IGST, CGST & SGST will be as follows in the chronological order:
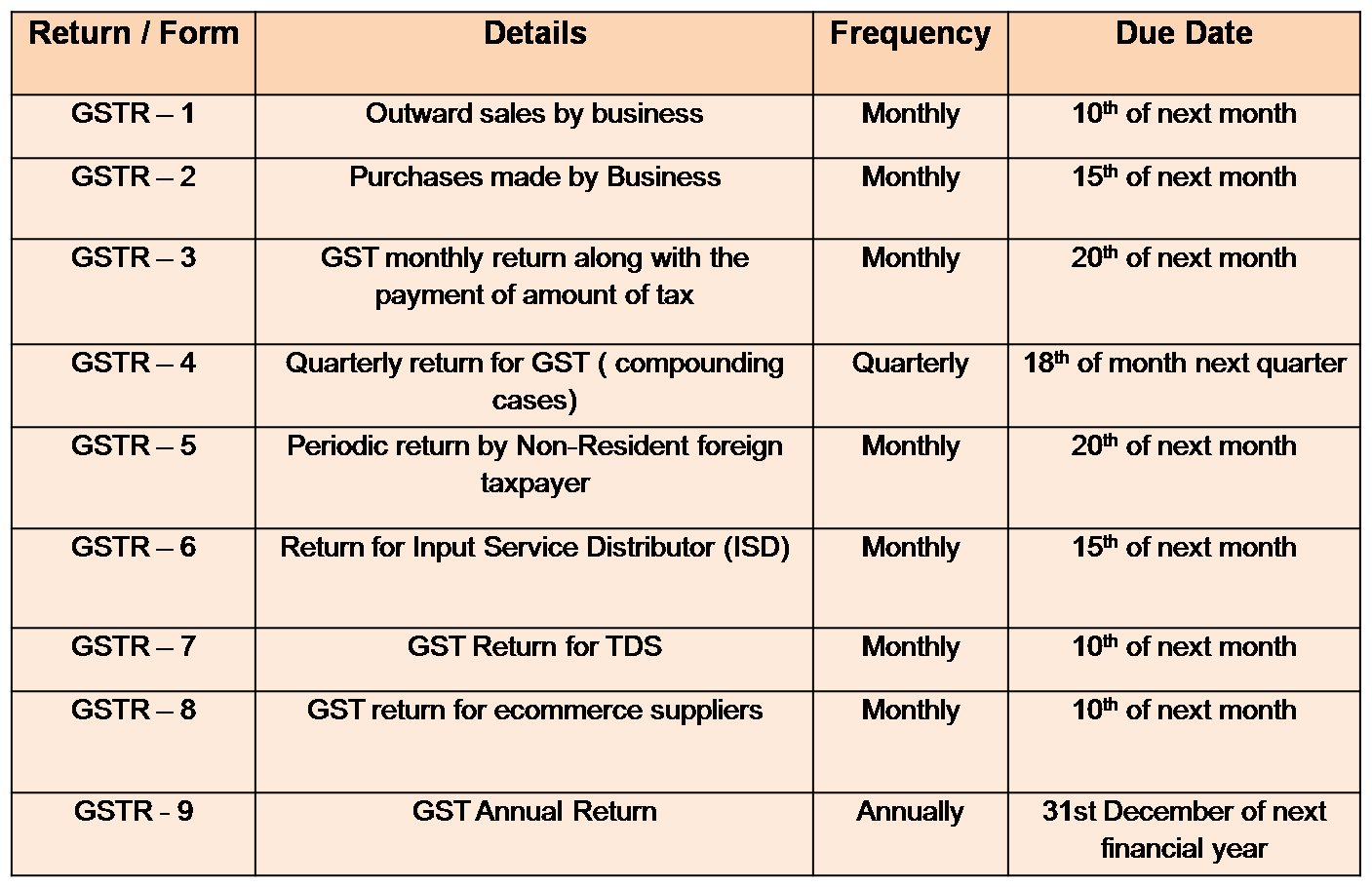
Returns under GST
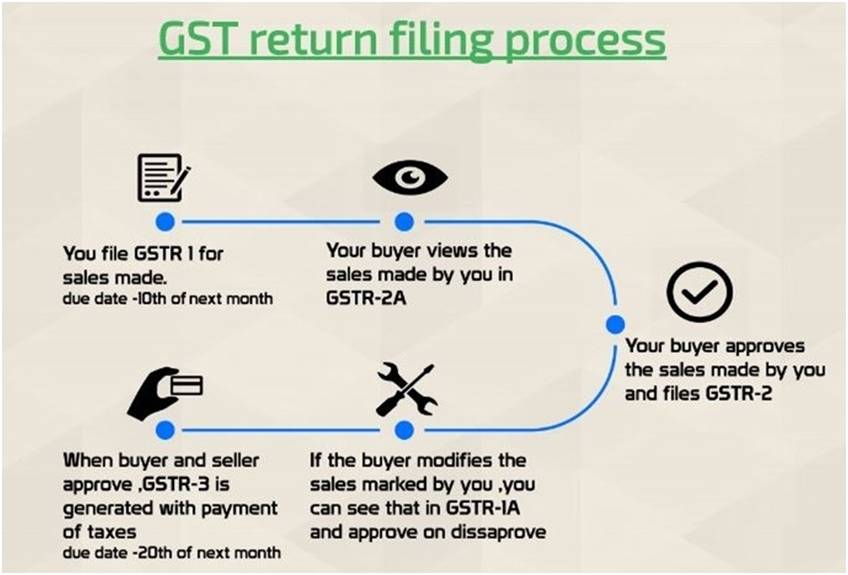
GST Return Filing Process
REFUND PROCESS UNDER GST
The procedure for processing of refund claim is as follows :
1.Application form for claiming refund can be filed through the GSTN portal.
2.An acknowledgement number would be shared with applicant via sms or email, once the application is filed electronically.
3.Adjustment would be made to return and cash ledger and reduce the “carry-forward input tax credit” automatically.
4.Refund application and documents submitted shall be scrutinized within a period of 30 days of filing the refund application.
5.Concept of “unjust enrichment” would be examined for reach refund application. If it does not qualify, then the refund would be transferred to CWF (Consumer Welfare Fund).
6.If refund claimed exceeds the predetermined amount of refund then it will go through pre-audit process for sanctioning the refund.
7.Refund will be credited electronically to the account of applicant via ECS, RTGS or NEFT.
8.Application for refund can be made at end of each quarter.
9.No refund shall be provided for an amount of less than Rs 1,000.
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR CLAIMING REFUND UNDER GST
As per Section 54 (4) –
The application shall be accompanied by—
(a) such documentary evidence as may be prescribed to establish that a refund is due to the applicant; and
(b) such documentary or other evidence (including the documents referred to in section 33) as the applicant may furnish to establish that the amount of tax and interest, if any, paid on such tax or any other amount paid in relation to which such refund is claimed was collected from, or paid by, him and the incidence of such tax and interest had not been passed on to any other person:
Provided that where the amount claimed as refund is less than two lakh rupees, it shall not be necessary for the applicant to furnish any documentary and other evidences but he may file a declaration, based on the documentary or other evidences available with him, certifying that the incidence of such tax and interest had not been passed on to any other person.
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR CLAIMING REFUND UNDER GST
CRUX –
1.If the amount claimed as tax refund is less than Rs. 5 Lakhs – The person needs to file a declaration, based on the documents or other evidence available with him, certifying that the incidence of tax or interest being claimed as refund has not been passed on to another person.
2.If the amount claimed as refund is more than Rs. 5 Lakhs – The application for refund must be accompanied by:
- a) Documentary evidence to establish that the refund is due to the person.
- b) Documentary or other evidence to establish that the amount was paid by him/her, and that the incidence of the tax or interest has not been passed on to another person.
GST Rates
On Services:
- Healthcare and education are exempt. Transportation to fall under 5 per cent bracket
- All services have been fitted into four different rates, which are 5%, 12%, the standard 18% and the luxury rate of 28%
- Travelling on metro, local train, religious travel, Haj yatra will all be exempt from GST
- AC train travel to get cheaper under GST
- Transport services (Railways, air transport) will be under the 5% category because their main input is petroleum, which is outside GST ambit.
- Service tax on non-AC hotels will 12%, on AC hotels that serve liquor will be 18%. Higher tax rate for luxury hotels.
- Hotels and lodges with tariff below Rs 1,000 will be exempt. Those with Rs 2,500-5,000 will be 18%. Luxury hotels will face tax of 28%. All hotel services with tariff over Rs 5,000 to be taxed at 28 per cent.
- 28% tax slab on 5-star hotels, race club betting, cinema.
- 18% tax slab for telecom, financial services
- E-commerce players to deduct tax at source before paying suppliers. E-retailers such as Flipkart and Snapdeal to pay GST.
- Restaurants with an annual turnover of less than Rs 50 lakh will fall under the 5 percent tax slab, while non-ACs food joints will be taxed at 12 percent. Air-conditioned restaurants with liquor licences will be taxed at 18 percent.
- Cinema halls were currently paying a service tax of 15 percent plus a state entertainment tax that ranged from 28 percent to about 100 percent. All these will be subsumed under the 28 percent GST rate, bringing out the costs of service significantly, Jaitley said. Casinos will also come under the 28 percent tax bracket.
-
Work contract services such as those paid by civil contractors for infrastructure construction currently pay a central tax of 6 percent, state taxes ranging from one to five percent, but without any input credit.
-
Mobile phones, fountain pen ink, tooth powder, incense sticks, feeding bottles, Braille paper, children’s colouring books, umbrellas, pencil sharpeners, tractors, bicycles, contact lenses, spectacle lenses, utensils, sports goods, fishing rods, combs, pencils and hand paintings have been placed under the 12% tax rate under GST.
-
Cheaper Services after GST – Radio taxi, Movies, Entertainment services , AC train travel, Air travel, Restaurants, Dhabas.
-
81% items to be taxed below 18% rate under GST: The Goods and Services Council today finalised tax rates for 1,211 items with a majority of items being kept in under 18 per cent rate slab.
-
Out of total 81 per cent items, exemptions have been given for 7% goods, while 14% goods are in 5% category; 17% goods are in 12% category; 43% goods in 18% category; and 19% goods in 28% category.
On Goods:
-
Sugar, Tea, Coffee (except Instant) and edible oil to fall under 5 per cent slab, while cereals, milk to be part of exempt list under GST
-
In a big boost to industry, Council has set the rate for capital good, industrial intermediate items at 18 per cent
-
Coal to be taxed at 5 per cent against current 11.69 per cent
-
Tooth paste, hair oil, soaps will be taxed at 18 per cent, it is being tax at 28 per cent, currently.
-
Common man items have gone into 12 per cent and 18 per cent slab
-
Indians sweets or mithai in 5 per cent slab.
-
Hair oil, toothpaste and soaps will be taxed at 18 percent under GST, significantly lower than the present effective rate of 28 percent.
-
Most exemptions for services to continue. Service tax, luxury tax will be subsumed in GST
-
GST rate for branded garments at 18 per cent
-
GST Council to mull beedi, cigarette, gold
-
Small cars will face 28% GST, along with a small cess, while luxury cars will attract 15% cess in addition of the tax.
-
Consumer durables such as AC and fridge too are in the 28% bracket, although officers said given the current incidence of 30-31%, there should be a reduction in prices.
GST Nil rate (0%):
No tax will be imposed on items like fresh meat, fish chicken, eggs, milk, butter milk, curd, natural honey, fresh fruits and vegetables, flour, besan, bread, prasad, salt, bindi. Sindoor, stamps, judicial papers, printed books, newspapers, bangles, handloom etc.
GST 5% Items List:
Items such as fish fillet, cream, skimmed milk powder, branded paneer, frozen vegetables, coffee, tea, spices, pizza bread, rusk, sabudana, kerosene, coal, medicines, stent, lifeboats will attract tax of 5 percent.
GST 12% Items list:
Frozen meat products , butter, cheese, ghee, dry fruits in packaged form, animal fat, sausage, fruit juices, Bhutia, namkeen, Ayurvedic medicines, tooth powder, agarbatti, colouring books, picture books, umbrella, sewing machine, and cellphones will be under 12 per cent tax slab.
GST 18% Items List:
Most items are under this tax slab which include flavoured refined sugar, pasta, cornflakes, pastries and cakes, preserved vegetables, jams, sauces, soups, ice cream, instant food mixes, mineral water, tissues, envelopes, tampons, note books, steel products, printed circuits, camera, speakers and monitors.
GST 28% Items list:
Chewing gum, molasses, chocolate not containing cocoa, waffles and wafers coated with chocolate, pan masala, aerated water, paint, deodorants, shaving creams, after shave, hair shampoo, dye, sunscreen, wallpaper, ceramic tiles, water heater, dishwasher, weighing machine, washing machine, ATM, vending machines, vacuum cleaner, shavers, hair clippers, automobiles, motorcycles, aircraft for personal use, and yachts will attract 28 per cent tax – the highest under GST system.
We have launched Single Platform on GST Compliances In India, assisting in 4 areas – 1) Migration, 2) GST Compliance, 3) Training and 4) Transition & Implementation. Click this link for any assistance.

 Toll Free:
Toll Free:  Contact Us
Contact Us